If your home is equipped with a gas range, you’re not alone. According to the US Energy Information Administration, around 38% of all American households use a natural gas stove, and it’s not hard to see why. People love cooking with gas because it’s highly responsive, cooks evenly, and is suited for many types of cookware. But could your gas stove be harming you and your loved ones?
A growing number of reports are coming out on news sites and science journals stating that gas ranges could be a problem for your health and the planet. In addition to concerns with CO emissions, people are now becoming alarmed about nitrogen oxides (NOx). NOx gases can aggravate existing health conditions and increase the risk of developing new problems. So should you kick your gas stove to the curb, or are there measures you can take to ensure your gas range is safe for you and your family? Read on to learn more.
How Do Gas Stoves Work?

To understand the potential issues with gas ranges, we first must understand how they work. Gas stoves rely on combustion. In other words, we tonight natural gas to create a source of heat for cooking. But a blue, heat-producing flame isn’t the only thing that gets produced by this chemical reaction. In addition, the burning gas from your stove is churning out pollutants that aren’t detectable to your sense of sight or smell. These microscopic particles can include Carbon Monoxide, Nitrogen Oxide, and Nitrogen Dioxide.
How Can Gas Stove Particles Impact Health?
So what’s the big deal with these particles? Although you probably know the potential risks associated with CO leaks and poisoning and have taken steps to mitigate those risks, you may not be aware of the problems that come from NOx. NOx, particularly Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2), are respiratory irritants. Short-term exposure can cause:
Longer-term exposure can lead to:
- Increased risk of developing asthma
- Interference with the ability of the blood to carry Oxygen
- Headaches
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
On top of everything else, gas stoves can also continuously emit benzene – a carcinogen. Exposure to benzene can cause:
- Increased risk of blood disorders
- Increased risk of cancer
- Potential reproductive issues
What Do the Latest Studies Say About Gas Stoves?
Gas stoves have been under much scrutiny as of late. While scientists have long known that the combustion process releases certain harmful gasses, chemicals, and particles into the air, this information has only recently come to the attention of the media and the public. While science has paid close attention to the effects of CO and NOx levels in outdoor environments, they haven’t gone public with standards for running a gas stove indoors. But that’s problematic, especially when you consider that testing as far back as 1985 revealed that a gas stove can release NOx at levels that exceed the outdoor standards set forth by the EPA. That means that millions of Americans are exposed to higher than acceptable levels of harmful gasses inside their own homes – typically an environment that is not well-ventilated.
In recent days, many of these findings have started to come to light. The media has been reporting on the dangers of using an indoor gas stove, causing some major cities like Berkley, California to place a total ban on gas ranges. Consumer Reports found that even running a single gas burner on “low” resulted in significantly elevated levels of Nitrogen Dioxide. They determined that the acute toxicity of Nitrogen Dioxide can cause health problems even within the span of normal meal prep and cooking. Another recent study by the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood indicates that gas cooking increases the risk of aggravating asthma in children by 42% and of developing asthma over a lifetime by 24%. All evidence seems to point to the same thing: left unchecked, gas stoves can wreak havoc on the health of your entire household.
Can My Carbon Monoxide Detector Mitigate Risk?
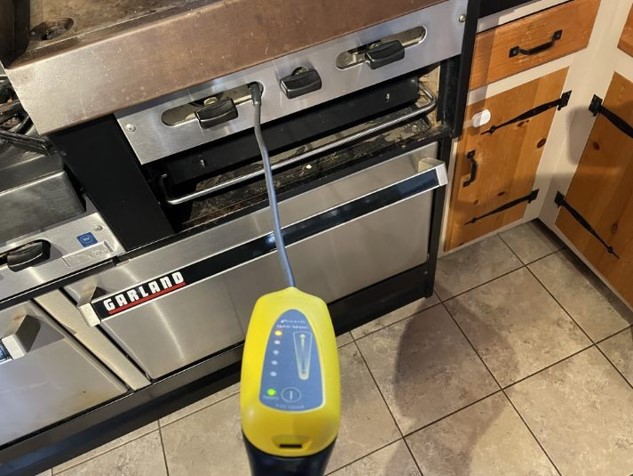

As mentioned previously, most households with a gas stove will also be equipped with a carbon monoxide detector. But while this is certainly a crucial part of monitoring CO detectors in your home, it’s not enough to protect you and your family. CO detectors may only go off in a life threatening situation often when the CO levels exceed 150 parts per million (ppm). Levels above 5 ppm may cause adverse health effects like headaches. Furthermore, carbon monoxide detectors will not pick up nitrogen dioxide, benzene, or other ultra-fine particulate matter. Specialized meters and detectors are required to accurately measure the levels of these gasses and particles in the air and to determine what steps need to be taken to improve health and safety within your home.
How Can I Ensure Safety in a Home with a Gas Stove?
Now that you understand the potential health risks associated with gas ranges, you don’t need to panic. While this is a serious matter that demands your attention, it’s important to stay calm and take proactive measures to assess your current level of exposure and mitigate risk going forward. Here are a few important steps to take:
- Hire a Professional to Evaluate Your Home – Begin by getting in touch with a qualified indoor air quality specialist like IndoorDoctor. While you don’t have the tools required to evaluate your situation adequately, we do. We use handheld gas meters, photo-ionizing detectors (PIDs), and laser particle scanners. These allow us to instantly measure the gas levels in your home, graph out low levels of CO that a standard home detector can’t measure, and detect NOx, volatile organic compounds, and ultra-fine particles. This will give us a fast read on your household’s current conditions.
- Try Virtual Testing – Although IndoorDoctor serves a wide range of cities throughout the US, you may live in an area out of our service range. This doesn’t mean you’re out of luck. Give us a call and talk to one of our experts about virtual testing. We can arrange to send out a kit, including the tools you need to evaluate your home. We’ll conference with you on a Zoom call to walk you through the process of using the tools and properly measuring your indoor air quality (IAQ). No matter where you are, we want to make sure you’re safe and healthy.
- Take an Air Sample – We further recommend having an air sample collected and sent into a laboratory for a more fine-tuned assessment of gasses and chemicals in your home. Labs can let you know how much of a substance is present in parts per billion, thus providing you with the most accurate information about whether or not your gas stove is safe.
- Properly Ventilate Your Space – One of the primary reasons why gas stoves can become so dangerous is that many kitchens lack proper ventilation. You can significantly mitigate risk and improve the health and safety of your living environment by installing a highly functioning range hood to vent harmful contaminants outside your home. During the warmer months, consider opening windows and doors to keep fresh air circulating throughout your space.
- Consider a Replacement – If, after completing an indoor air quality assessment and receiving feedback on an air sample, you learn that your stove is emitting a lot of dangerous gasses, chemicals, and particulate matter, you may simply want to consider trading in your old gas stove for an electric or convection range.
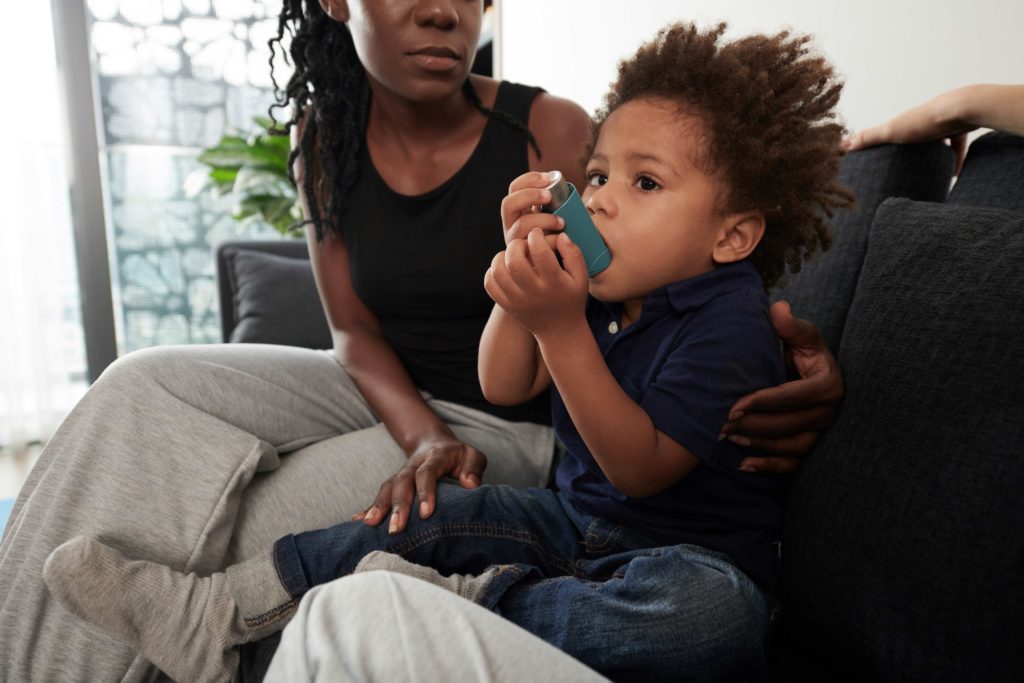

Are There Other Dangerous Sources of Gases and Particles I Should Know About?
Gas stoves may be under fire as of late, but are they the only point of origin for harmful gasses, chemicals, and particles that you should be concerned about? Well, hardly. The average American home is filled with potential sources of health hazards that can reduce IAQ. You should be on high alert if your household relies on any appliance that utilizes natural gas, coal, oil, or wood. For instance, a wood-burning or pellet stove can release harmful levels of Nitrogen Dioxide, particulate matter, and Carbon Monoxide. All these can aggravate existing health conditions while increasing the risk of developing lung and breathing disorders or even certain cancers. Water heaters relying on gas could also emit dangerous gasses and chemicals. Of course, gas clothes dryers and poorly ventilated or insulated attached garages are notorious for being a source of CO poisoning. Finally, if anyone in the home smokes tobacco, be advised that your home likely has high levels of NOx and other dangerous chemicals that can lead to serious health issues. Understanding these potential health hazards is important in evaluating your home and taking steps to mitigate risk and improve your IAQ. While having your gas stove tested, it’s a good idea to test your whole home for problems and to work with a professional to devise a plan to improve the quality of the air you breathe each day.
Start Breathing and Living Better Today
If you have any concerns whatsoever about the safety of your gas stove, don’t hesitate to reach out to IndoorDoctor. We’re here to help you test your Indoor Air Quality and take measures to improve health conditions for you and your household. Give us a call to schedule your consultation today.
References
- In 2020, most U.S. households prepared at least one hot meal a day at home
- Gas stoves can harm your health — and scientists have known that for decades
- Is Your Gas Range a Health Risk?
- Cooking fuels and prevalence of asthma: a global analysis of phase three of the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC)






